VPN Services for Privacy: A Comprehensive Guide unveils the crucial role of Virtual Private Networks in safeguarding your digital life. In today’s interconnected world, online privacy is increasingly threatened by data breaches, surveillance, and malicious actors. This guide explores the intricacies of VPN technology, detailing how it protects your data, masks your IP address, and enhances your online anonymity. We’ll delve into selecting a reputable VPN provider, understanding their limitations, and navigating the legal landscape surrounding their use. Ultimately, this guide empowers you to make informed decisions about protecting your online privacy.
Introduction to VPN Services and Online Privacy
In today’s interconnected world, online privacy is a paramount concern. The increasing reliance on the internet for communication, commerce, and information access exposes individuals and organizations to a multitude of threats. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) offer a powerful technological solution to mitigate these risks, enhancing online security and anonymity. This section will explore the fundamentals of VPN technology, the prevalent threats to online privacy, and the key benefits of utilizing VPN services.
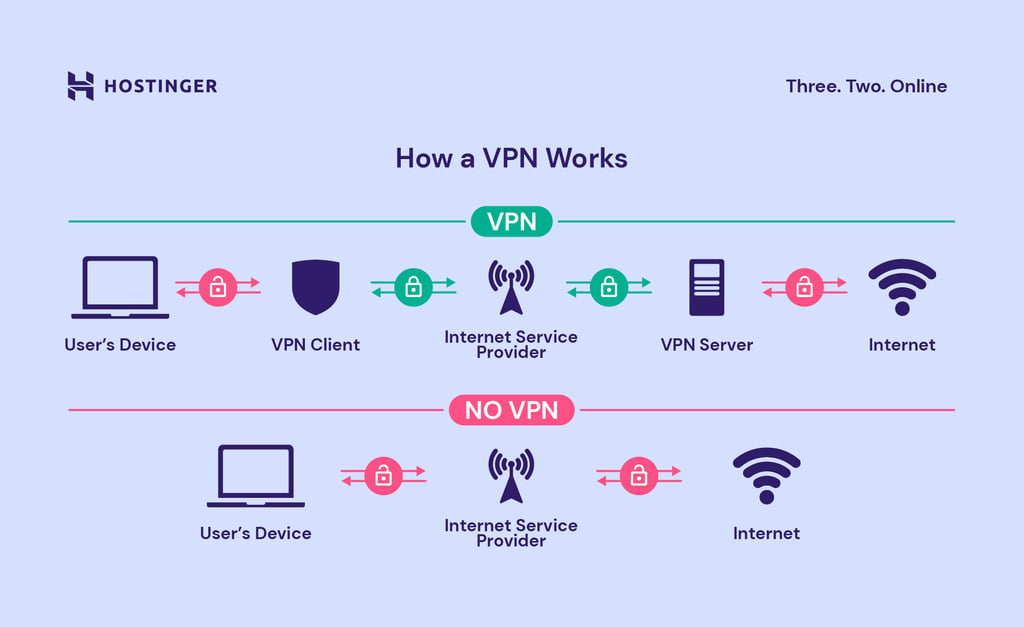
VPN technology essentially creates a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the internet. This encrypted tunnel protects your data from prying eyes, masking your IP address and encrypting your online activity. Think of it as a private, secure line running through a public network. This encryption makes it significantly more difficult for hackers, governments, or internet service providers (ISPs) to intercept your data or track your online behavior. The process involves routing your internet traffic through a VPN server, changing your apparent location and making it harder to trace your activity back to you.
Threats to Online Privacy
The digital landscape presents a multitude of threats to online privacy. These threats range from everyday inconveniences to serious security breaches with potentially devastating consequences. Data breaches, where sensitive personal information is stolen, are a major concern. These breaches can expose everything from financial details and medical records to social security numbers and passwords. Furthermore, government surveillance and corporate data collection practices can lead to the tracking and profiling of individuals’ online activities. Malicious actors, such as hackers and cybercriminals, also pose a significant threat, using sophisticated techniques to gain unauthorized access to personal information and systems. Finally, unsecured Wi-Fi networks, commonly found in public places like cafes and airports, are vulnerable to eavesdropping, allowing attackers to intercept unencrypted data.
Benefits of Using VPN Services
Utilizing a VPN service offers several key benefits for enhancing online security and anonymity. Firstly, VPNs encrypt internet traffic, protecting sensitive data from interception by unauthorized parties. This is crucial for activities like online banking, shopping, and communication, safeguarding personal and financial information. Secondly, VPNs mask your IP address, concealing your true location and making it more difficult to track your online activities. This is particularly valuable for users who wish to access geographically restricted content or maintain anonymity while browsing the internet. Thirdly, VPNs can enhance security on public Wi-Fi networks, providing an extra layer of protection against eavesdropping and man-in-the-middle attacks. By encrypting your connection, a VPN prevents others from accessing your data while you are using a public Wi-Fi network. Finally, some VPN services offer additional features like ad blockers and malware protection, further enhancing online security and privacy.
How VPNs Protect Your Privacy
VPNs, or Virtual Private Networks, offer a crucial layer of security and privacy online by creating an encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet. This effectively masks your IP address, encrypts your data, and prevents third parties from monitoring your online activities. Understanding the technical mechanisms behind this protection is key to appreciating the benefits a VPN provides.
VPNs achieve this protection through a combination of encryption and IP address masking. Encryption scrambles your data, rendering it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it. The VPN server acts as an intermediary, receiving your encrypted data, decrypting it, and then sending it to your destination. The return traffic follows the same process in reverse. This ensures that your browsing history, downloads, and other online activities remain private. Simultaneously, the VPN masks your real IP address by assigning you a temporary IP address from the VPN server’s location. This prevents websites and other online services from tracking your location and identifying your device.
VPN Encryption Protocols and Their Strengths
Different VPN providers utilize various encryption protocols, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The choice of protocol significantly impacts the security and speed of your connection. Stronger encryption offers better protection but might result in slightly slower speeds.
- OpenVPN: Widely considered a robust and secure protocol, OpenVPN uses SSL/TLS encryption and offers a high level of flexibility and customization. It’s known for its strong security and open-source nature, allowing for independent audits and verification of its security.
- WireGuard: A newer protocol, WireGuard is praised for its speed and simplicity. While still relatively new, it’s gaining popularity due to its improved performance compared to older protocols like OpenVPN, while maintaining a strong security profile. Its leaner design makes it faster and easier to implement.
- IKEv2/IPsec: This protocol offers a good balance between security and speed, making it a popular choice for mobile devices. It’s particularly adept at handling network changes, making it suitable for users who frequently switch between Wi-Fi and cellular data.
- PPTP: An older protocol, PPTP is generally considered less secure than modern options. While faster, its outdated encryption standards make it vulnerable to attacks. It’s generally not recommended for sensitive online activities.
Security Features Offered by Different VPN Providers
The security features offered by different VPN providers vary significantly. Factors such as the encryption protocols used, the presence of a kill switch (which cuts your internet connection if the VPN drops), and the provider’s no-logs policy all contribute to the overall security. Some providers also offer additional features like split tunneling (routing only specific apps through the VPN), DNS leak protection (preventing your DNS requests from revealing your real IP address), and multi-hop connections (routing your traffic through multiple VPN servers for enhanced anonymity).
| VPN Provider Feature | Example Provider 1 | Example Provider 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption Protocols | OpenVPN, WireGuard, IKEv2 | OpenVPN, WireGuard |
| Kill Switch | Yes | Yes |
| No-Logs Policy | Claimed | Audited |
| Split Tunneling | Yes | No |
Choosing a VPN provider requires careful consideration of these features. Reading independent reviews and examining the provider’s privacy policy are crucial steps in ensuring you select a VPN that adequately protects your privacy.
Choosing the Right VPN Service
Selecting a VPN provider requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure your online privacy and security are adequately protected. A poorly chosen VPN can offer little to no benefit, potentially even exposing you to greater risks. This section will guide you through the essential aspects to evaluate before subscribing to a VPN service.
Key Factors in VPN Provider Selection
Choosing a VPN involves assessing various critical aspects. Security features, privacy policies, and the provider’s jurisdiction all play significant roles in determining the effectiveness and trustworthiness of a VPN service. A strong security protocol is essential, but equally important is a robust privacy policy that protects user data. The jurisdiction of the VPN provider also matters, as different countries have varying data retention laws. Providers located in countries with strong privacy protections are generally preferred.
VPN Service Comparison
The following table compares four reputable VPN services across several key metrics. Note that speeds and server counts can fluctuate, and these figures represent typical performance at the time of writing. Always check the latest information on the provider’s website.
| Provider | Price (Approximate Monthly) | Server Count (Approximate) | Encryption Protocol |
|---|---|---|---|
| NordVPN | $3-$12 | 5500+ | AES-256-GCM |
| ExpressVPN | $6-$10 | 3000+ | AES-256-CBC |
| Surfshark | $2-$12 | 3200+ | AES-256-GCM |
| ProtonVPN | $4-$24 | 1400+ | AES-256-GCM |
Importance of a No-Logs Policy
A strict no-logs policy is paramount for user privacy. This policy means the VPN provider does not store any data about your online activities, such as websites visited, data downloaded, or IP addresses used. Without a verifiable no-logs policy, your anonymity and privacy are compromised, as the provider could potentially hand over your data to third parties, including governments, upon request. Many providers claim a no-logs policy, but independent audits and transparent data handling practices are crucial for ensuring the validity of such claims. For example, a provider undergoing regular independent audits by reputable security firms provides a stronger assurance of their no-logs commitment compared to those without such verification. The implications of a lack of a robust no-logs policy can range from targeted advertising to potential legal ramifications for users depending on their online activities and the jurisdiction of the VPN provider.
VPNs and Different Online Activities
VPNs significantly enhance online privacy and security across various digital activities. Their versatility extends beyond simple browsing, offering robust protection in diverse online environments. This section explores how VPNs benefit users engaging in common online tasks, from accessing public Wi-Fi to streaming and online banking.
VPNs and Public Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi networks, while convenient, often lack robust security measures, making them vulnerable to eavesdropping and data breaches. A VPN creates a secure, encrypted tunnel between your device and the internet, shielding your data from prying eyes on shared networks. This means your browsing history, login credentials, and other sensitive information remain private, even when connected to an unsecured public Wi-Fi hotspot at a coffee shop, airport, or hotel. Data transmitted through this encrypted tunnel is unreadable to anyone intercepting the signal. For example, if you’re checking your bank account balance on public Wi-Fi with a VPN enabled, your banking details are protected from potential attackers.
VPNs and Streaming Services
VPNs offer significant advantages for users of streaming services. Many streaming platforms utilize geo-restrictions, limiting content availability based on the user’s location. By connecting to a VPN server in a different country, users can bypass these restrictions and access a wider range of movies, TV shows, and other content. For example, a user in the United States might use a VPN to connect to a server in the United Kingdom to access content exclusive to UK viewers on BBC iPlayer. Additionally, VPNs can help protect user privacy by masking their IP address from the streaming service, preventing the service from tracking their viewing habits.
VPNs and Online Banking and Shopping
Online banking and shopping require a high level of security to protect sensitive financial information. Using a VPN adds an extra layer of protection by encrypting your connection, making it significantly more difficult for hackers to intercept your data, even on otherwise secure websites. For instance, when accessing your online banking portal, a VPN encrypts your login credentials and transaction details, preventing malicious actors from stealing your financial information. Similarly, when shopping online, a VPN safeguards your credit card details and personal information during transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and identity theft. The encrypted connection makes it significantly harder for anyone monitoring your network to see what you’re buying or the details of your payment.
Understanding VPN Limitations and Potential Risks
While VPNs offer significant privacy and security benefits, it’s crucial to understand their limitations and potential risks to make informed decisions. Not all VPNs are created equal, and relying on one without a full understanding of its capabilities and drawbacks can leave you vulnerable. This section explores these crucial aspects.
VPNs, while enhancing your online privacy, aren’t a silver bullet. They introduce certain trade-offs, and using them incorrectly can negate their protective effects. Understanding these limitations is key to maximizing their effectiveness and mitigating potential risks.
Speed Reduction
Using a VPN can slow down your internet speed. This is because your data travels a longer distance – to the VPN server and then to its destination – and the encryption process adds computational overhead. The degree of slowdown varies depending on factors such as the VPN server’s location, its load, your internet connection speed, and the encryption protocol used. For instance, a user streaming 4K video might experience noticeable buffering if connected to a distant server with high traffic. Choosing a VPN with a robust server network and optimizing your VPN settings can help mitigate this issue.
Potential Vulnerabilities
While VPNs encrypt your data, they are not foolproof. A poorly designed or configured VPN can introduce vulnerabilities. For example, a VPN provider with weak encryption standards or inadequate security practices could leave your data susceptible to interception. Furthermore, some VPNs might log your activity, contradicting their purpose of enhancing privacy. This emphasizes the importance of choosing a reputable provider with a proven track record of strong security practices. A vulnerability in the VPN software itself could also compromise your security, highlighting the need for regular updates and security audits by the provider.
Risks Associated with Free or Unreliable VPN Providers
Free VPN services often come with significant drawbacks. Many lack robust security measures, may log user data for marketing or other purposes, and might even inject malware into your system. Unreliable providers might sell your data to third parties, defeating the purpose of using a VPN in the first place. Furthermore, free VPNs frequently have limited server locations, slower speeds, and data caps, significantly impacting user experience. For example, a free VPN might limit your bandwidth to a few gigabytes per month, making it unsuitable for heavy data users. The lack of transparency regarding data logging policies is also a serious concern with these providers.
Importance of Choosing a Reputable VPN Provider
Selecting a reputable VPN provider with a strong security track record is paramount. Reputable providers typically employ strong encryption protocols, maintain a strict no-logs policy, undergo regular security audits, and have transparent privacy policies. They often offer robust customer support and a wide range of server locations to ensure optimal performance and security. Researching user reviews, checking for independent security audits, and examining the provider’s privacy policy are crucial steps in selecting a reliable VPN service. For instance, a provider with a proven track record of resisting government requests for user data would be considered more trustworthy than one with a history of compliance.
Setting Up and Using a VPN
Setting up a VPN is generally straightforward, though the specific steps vary slightly depending on your operating system and chosen VPN provider. This section provides a guide to installing and configuring a VPN on common devices, along with best practices for secure usage. Remember to always download VPN software directly from the provider’s official website to avoid malicious downloads.
The process typically involves downloading the VPN client, creating an account (if you haven’t already), installing the software, logging in, and selecting a server location. After this, your internet traffic will be encrypted and routed through the VPN server, masking your IP address and encrypting your data.
VPN Installation and Configuration on Different Devices
This section details the general steps for installing and configuring a VPN on various operating systems. Specific instructions may vary depending on the VPN provider.
Regardless of the operating system, the core process remains similar: download the application from the provider’s website, install it, create an account (if necessary), log in, and select a server location. After successful connection, you should see a notification indicating the VPN is active and your new IP address.
- Windows: Download the VPN client from the provider’s website, run the installer, follow the on-screen prompts, and log in using your credentials. Choose a server location and connect. Windows often has built-in VPN support, but using the provider’s dedicated client is recommended for optimal performance and security features.
- macOS: Similar to Windows, download the VPN client from the provider’s website, run the installer, and follow the on-screen instructions. Login using your account details, select a server, and connect. macOS also offers built-in VPN capabilities, but the provider’s application usually provides a more streamlined and feature-rich experience.
- iOS (iPhone/iPad): Download the VPN app from the App Store. Install the app, open it, log in with your account credentials, and choose a server location. iOS’s user-friendly interface makes the setup process intuitive.
- Android: Download the VPN app from the Google Play Store. Install the app, open it, log in using your account details, and select a server. Android’s flexibility allows for a wide range of VPN apps, ensuring compatibility across diverse devices.
Connecting to a VPN Server: A Flowchart
The following flowchart illustrates the typical steps involved in connecting to a VPN server. Note that specific steps and terminology might vary slightly depending on your VPN provider and device.
Imagine a flowchart with the following steps represented visually using boxes and arrows:
- Start: The beginning of the process.
- Open VPN Client: Launch the VPN application on your device.
- Login: Enter your username and password.
- Select Server: Choose a server location from the list provided by your VPN provider.
- Connect: Initiate the connection to the selected server.
- Verify Connection: Check if the connection is successful. This is often indicated by a status change in the VPN client and/or a change in your IP address.
- End: The connection is established and your internet traffic is now routed through the VPN server.
Best Practices for Maintaining VPN Security
Maintaining the security of your VPN connection is crucial to ensure your privacy and online safety. Following these best practices will significantly reduce the risk of potential breaches.
- Use Strong Passwords: Employ complex and unique passwords for your VPN account and other online accounts. Consider using a password manager to generate and securely store these passwords.
- Keep Your VPN Software Updated: Regularly update your VPN client to benefit from the latest security patches and bug fixes. Outdated software can be vulnerable to exploits.
- Choose Reputable VPN Providers: Select a VPN provider with a strong reputation for security and privacy. Research providers thoroughly before making a decision.
- Use a Kill Switch: Enable the kill switch feature in your VPN client. This feature automatically cuts off your internet connection if the VPN connection drops, preventing your real IP address from being exposed.
- Avoid Public Wi-Fi Without a VPN: Public Wi-Fi networks are often insecure. Always use a VPN when connecting to public Wi-Fi to protect your data from potential eavesdroppers.
- Regularly Review Your VPN Settings: Periodically check your VPN settings to ensure they are configured optimally for your security needs. Consider reviewing your chosen protocols and encryption levels.
VPN and Legal Considerations
Using a VPN, while offering significant privacy benefits, introduces a layer of legal complexity that varies considerably across different jurisdictions. Understanding these legal implications is crucial for responsible and safe VPN usage. Failure to do so could lead to unintended consequences, ranging from account suspension to legal repercussions.
The legality of VPN use is not universally consistent. While many countries have no specific laws prohibiting VPN use, others have implemented strict regulations or outright bans. These regulations often stem from concerns about circumventing censorship, evading taxes, or facilitating illegal activities. The specific legal landscape can also be impacted by the user’s activities while connected to a VPN, making it a nuanced area requiring careful consideration.
VPN Legality by Country
The legal status of VPNs varies greatly depending on the country’s laws and political climate. Some countries actively monitor and restrict VPN usage, while others have more lenient regulations. This variability necessitates careful research before using a VPN in a particular region.
- China: China has strict regulations on VPN use, requiring VPN providers to obtain licenses and users to use only approved VPNs. Unauthorized VPN use can result in fines or even imprisonment.
- Russia: Russia also has regulations regarding VPN use, with a focus on monitoring and controlling access to information. Unauthorized VPN use can lead to penalties.
- United Arab Emirates (UAE): The UAE has regulations regarding VPN use, particularly concerning content that violates local laws and customs. Using a VPN to access prohibited content can result in legal consequences.
- Turkey: Turkey has implemented restrictions on VPN use, aiming to control online access and content. Unauthorized VPN use can lead to penalties.
- Iran: Iran has strict regulations and often blocks access to many websites and services. Using a VPN to bypass these restrictions can be considered a violation of the law.
Potential Legal Concerns Related to VPN Usage
Several scenarios can raise legal concerns regarding VPN usage, even in countries without explicit VPN bans. These scenarios often involve the intersection of VPN use and illegal activities.
- Copyright Infringement: Using a VPN to access copyrighted material illegally, such as streaming movies or downloading music without permission, can lead to legal action from copyright holders.
- Online Fraud and Criminal Activity: VPNs can be used to mask the identity of individuals engaging in online fraud, scams, or other criminal activities. This can lead to severe legal consequences if detected.
- Circumventing Geo-Restrictions for Illegal Purposes: While many use VPNs to access geo-restricted content legitimately, using a VPN to access services or engage in activities prohibited in a specific location can lead to legal issues.
- Data Breaches and Privacy Violations: While VPNs enhance privacy, using them to access or share sensitive data illegally or to violate data privacy regulations can result in significant legal problems.
Recommendations for Legally Compliant VPN Use
To mitigate legal risks associated with VPN usage, it’s essential to understand and comply with the laws of the jurisdiction where you are using the VPN. This includes researching local regulations, choosing a reputable VPN provider with a clear privacy policy, and avoiding any activities that violate local laws while connected to a VPN. Always prioritize responsible and legal online behavior.
Future Trends in VPN Technology
The landscape of VPN technology is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in cryptography, network infrastructure, and user demands for enhanced privacy and security. Several emerging technologies and trends promise to significantly impact how VPNs function and are utilized in the coming years. These developments will likely lead to faster, more secure, and more user-friendly VPN experiences.
The future of VPNs will be shaped by a convergence of several key technological advancements. These include improvements in encryption algorithms, the rise of mesh networks, and the increasing sophistication of privacy-enhancing techniques. Furthermore, the ongoing battle between VPN providers and those seeking to circumvent them will drive innovation on both sides.
Advancements in Encryption and Security Protocols
The core of any VPN’s effectiveness lies in its encryption. Current widely used protocols like OpenVPN and WireGuard are constantly being refined and improved. We can expect to see the adoption of post-quantum cryptography, designed to withstand attacks from quantum computers, becoming more prevalent. This will be crucial as quantum computing technology matures. Furthermore, research into more efficient and secure key exchange mechanisms will continue, potentially leading to faster connection speeds without compromising security. The development of new protocols specifically designed for mobile devices and IoT (Internet of Things) environments is also likely, addressing the unique challenges these present. For example, a hypothetical protocol might prioritize low latency and power efficiency over sheer cryptographic strength for smaller devices with limited processing power.
The Rise of Mesh Networks and Decentralized VPNs
Traditional VPNs rely on a central server infrastructure, creating a single point of potential failure and vulnerability. Decentralized VPNs, utilizing mesh network technology, offer a more resilient and privacy-focused alternative. In a mesh network, users connect directly to each other, distributing the load and minimizing reliance on a central server. This architecture makes it more difficult for a single entity to monitor or control the network traffic. The adoption of blockchain technology could further enhance the security and transparency of these decentralized VPNs, providing verifiable proof of connection and encryption. A practical example could be a decentralized VPN used by activists in a country with strict internet censorship; the distributed nature would make it harder for authorities to shut down the entire network.
Increased Integration with Other Privacy Tools
We anticipate a greater integration of VPNs with other privacy-enhancing technologies. This could include seamless integration with Tor, allowing users to combine the anonymity of Tor with the speed and security of a VPN. Furthermore, we can expect to see tighter integration with privacy-focused browsers and operating systems, streamlining the user experience and enhancing overall security. For instance, a future operating system might offer a built-in VPN option with pre-configured settings for different levels of security and anonymity, simplifying the process for average users.
Evolution of VPN Usage
The use of VPNs is expected to continue its upward trajectory, driven by increasing concerns about online privacy and security. The growth of remote work and the increasing reliance on cloud services will further fuel this demand. We can expect to see more sophisticated VPN applications emerge, offering personalized security settings and advanced features like split tunneling (routing only specific applications through the VPN) and automatic server selection based on user location and network conditions. For example, a user could configure their VPN to automatically route their work traffic through a secure server while allowing their personal browsing to use their local network. This nuanced approach will cater to the diverse needs of users in a rapidly evolving digital landscape.
Final Conclusion
Securing your online privacy is paramount in the digital age, and understanding VPN services is a crucial step in that process. This comprehensive guide has equipped you with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of VPN technology, choose a reliable provider, and utilize VPNs effectively to enhance your online security and anonymity. By understanding both the benefits and limitations, you can confidently leverage VPNs to protect your sensitive data and maintain your privacy in an increasingly interconnected world. Remember to always prioritize reputable providers with strong security measures and transparent privacy policies.